
Gold stocks have moved above the AI-driven chips rally with a 135% gain in 2025, which reflects that the actual value of a stock might be hidden behind market price trends. But is this a fundamental increase or just hype?
Knowing how to calculate stock valuation helps investors to identify undervalued stocks, avoid overpriced stocks, and make appropriate investment decisions.
This blog helps to understand stock valuation and how to use valuation methods like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) and Dividend Discount Model (DDM), and ratios to make value-based decisions.
What Is Stock Valuation & Why It Matters
Stock valuation is the process of calculating the intrinsic or fundamental value of a share or stock of a company, irrespective of its market value. The stock valuation concept aims to calculate the intrinsic value, which could be the underlying value of a company’s shares.
Stock valuation matters because:
- Value-based Decisions: It helps to understand whether to invest in a particular stock. It helps to identify undervalued stocks and opportunities for investments.
- Maximise Returns: Valuation helps investors to focus on the long-term potential of stocks. Investors can purchase undervalued stocks at lower prices and maximise returns over time.
- Risk management: Stocks with high prices don’t always reflect strong valuation. It might be the result of speculation. Understanding the true value helps in avoiding overpriced stocks, which could carry high risk.
How to Calculate Stock Valuation
Learn the methods of valuation that investors use to analyse a company’s intrinsic value and decide whether a stock is rightly priced, undervalued, or overvalued. An AI assistant like Stoxo can assist investors in evaluating and comparing stocks more effectively.
Absolute (Intrinsic) Valuation Methods
These methods estimate the actual value of a stock by using the financial data and performance of a company.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Discounted cash flow (DCF) measures the time value of money which is widely used by investors to make investment decisions, while companies use it for capital budgeting and structuring costs.
DCF = CF1/(1+r)^1 + CF2/(1+r)^2 + … + CFn/(1+r)^n
Here, CF1, CF2, and CF3 represent cash flow for years one, two, and three, respectively, and r is the rate of discount.
Dividend Discount Model (DDM)
The Dividend Discounted Model (DDM) estimates the intrinsic value by discounting the total sum of expected dividend payments to the present value of the stock.
The Gordon Growth Model (Constant Growth Model), is the most widely used DDM method. It is calculated as,
P = D₁ / (r-g)
Here, P = intrinsic value, D₁ = expected dividend, r = rate of return, and g = growth rate of dividend.
Relative Valuation Techniques
These techniques compare the value of a company with its competitors to measure stock valuation across the sector.
P/E, P/B, P/S, EV/EBITDA Multiple
Price-to-earnings or P/E ratio is used to calculate how much an investor is willing to pay for each ₹1 of what the company earns. It is calculated as,
P/E ratio = Market Price/Earnings per share (EPS)
Price-to-book value or P/B ratio is calculated by comparing the market value of a stock to its book value, to identify whether the stock is rightly priced, undervalued, or overpriced.
P/B ratio = Market Price/Book Value
Price-to-sales or P/S ratio is a metric used to estimate how much an investor is willing to pay for each ₹1 of the company’s revenue. It is calculated as,
P/S ratio = Market price/Revenue
EV/EBITDA multiple metric is calculated by dividing the enterprise value of a company by EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortisation).
Enterprise value = Market capitalisation + Total Debt – Cash and cash equivalents
EV/EBITDA = Enterprise Value/EBITDA
Advanced Ratios & Formulas
The Price/Earnings-to-Growth (PEG) ratio is an advanced valuation metric, used for refining the Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio by using the growth rate of earnings per share for a particular period. It is calculated as,
PEG ratio = (P/E ratio)/ Earnings per share (EPS) Growth Rate
The Graham Number calculates the maximum price investors are willing to pay for a company’s share. It is calculated as,
Graham Number = 22.5 x Earnings per share x Book value of each share
The book value of shares can be calculated as,
Book Value = Shareholders’ equity/Outstanding shares
Comparative & Cyclical Metrics
Cyclical metrics measure both market movements and long-term economic trends.
The Cyclically Adjusted Price-to-earnings (CAPE) ratio, or Shiller P/E ratio, is a metric which helps investors evaluate whether a stock or market index is undervalued or overpriced.
CAPE incorporates earnings for a period of at least 10 years, whereas P/E only incorporates a single year’s earnings.
CAPE = Current Share Price/Inflation-adjusted earnings, on the basis of 10-year averages
Stock Valuation in Practice: Step-by-Step
The core idea of stock valuation for investors is to find stocks that are undervalued, to maximise returns. Let’s understand step-by-step how to calculate stock valuation.
Step 1: Fundamental analysis, along with industry and economic analysis, helps investors understand the company’s performance and financial health and the competitive advantage it holds in the industry under the given economic conditions.
Step 2: Select a valuation method based on the company’s stage in the business cycle, market stability, and industry. DCF calculates the intrinsic value based on future cash flows, while DDM is based on the total sum of future dividend payments to their present value.
Step 3: Upon estimating the intrinsic value, investors can make their decision regarding whether to invest in that particular stock or company.
Choosing the Best Method: Use Case
The best method for stock valuation depends on the type of company, investment goals, and, most importantly, available information and data.
Here’s how to select the best method for stock valuation.
| Use Case | Method | Why it works |
| For comparison within the industry | Relative valuation metrics such as P/E, P/B and P/S ratio. | Used for Comparing stock value of a company to the competitors’ stock value. |
| Industry analysis | Comparative metrics such as EV/EBITDA, P/E, etc. | Provides a benchmark for an industry. |
| For dividend paying companies | Dividend Discount Model (DDM) | Helps to analyse growth prospects and consistency of dividend payments. |
| Asset focused Companies | Asset based valuation, for example Market value = Total Asset – Total Liabilities. | Focus on physical assets of the company while deducting liabilities. |
| High growth companies or startups | Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) | Helps to calculate the intrinsic value of a stock |
Stoxo can assist by identifying the right valuation method, calculating ratios like P/E, P/B, and EV/EBITDA, and generating AI-based insights to guide investment decisions.
Here’s an example of the upcoming Lenskart IPO stock valuation by Stoxo. Mentioned below are the results shown by Stoxo:

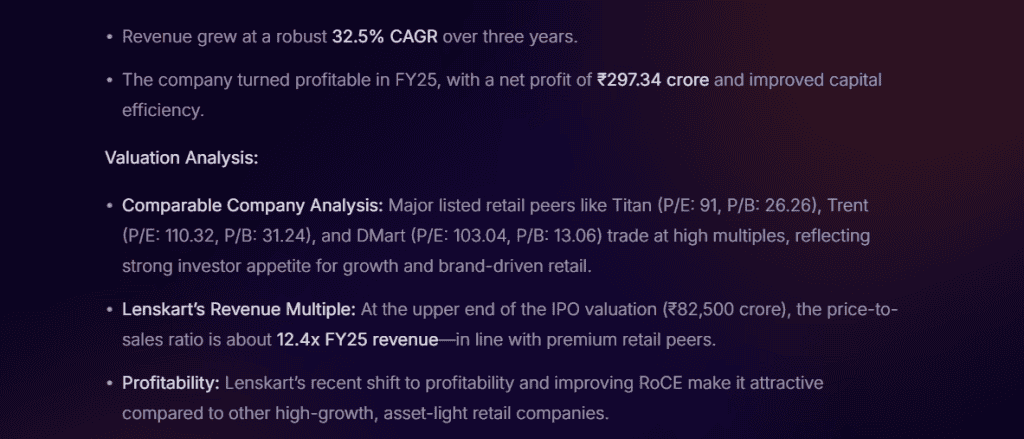

This represents the key financial details and valuation metrics, valuation analysis, and industry and market positioning. This helps investors to have an overview of the current business landscape and make necessary decisions.
Conclusion
The primary goal of stock valuation is to help investors identify undervalued opportunities and avoid overpriced stocks, which might be driven by speculation. By using the right valuation methods, such as Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Dividend Discount Model (DDM), and relative techniques like P/E, P/B, PEG, and CAPE, investors can make informed, value-based decisions.
Stock market AI tools like Stoxo simplify this process through data-driven analysis and AI insights.
FAQs
The methods used for calculating stock valuation comprise Absolute valuation methods, such as Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) and Dividend Discount Model (DDM), and Relative Valuation using ratios such as P/E, P/B, and P/S, and advanced metrics such as PEG, Graham Number, and CAPE.
The intrinsic value of a stock is calculated by using Absolute Valuation Methods, which are DCF and DDM, for estimating the actual value of a stock based on cash flows or expected dividend payments.
The discounted cash flow (DCF) calculates the expected cash flows of a company and discounts them to the present value by using a discount rate which reflects the time value of money.
The Dividend Discount Model (DDM) calculates the intrinsic value of a stock by discounting the total sum of expected dividend to the present value. The most commonly used method for DDM is Gordon Growth Model.
The most common valuation ratios are Price-to-Earnings (P/E), Price-to-Book (P/B), Price-to-Sales (P/S), and Price/Earnings-to-Growth (PEG). Each of them offers a comparison of value to a company’s competitors.
The relative valuation of a stock compares metrics like P/E, P/B, P/S, or EV/EBITDA of a company with similar companies in the same sector to identify undervalued or overpriced stocks.
Relative Valuation using ratios, which are P/E and P/B ratios, is the easiest way to calculate stock value for beginners, before advancing to detailed techniques such as DCF or DDM.

Leave a Comment