
With many different timeframes, strategies, and instruments, options trading can feel overwhelming. Many investors consider options as quick strategies for hedging or guesswork, but there’s another category designed for traders, willing to stay for a long time: LEAPS options trading.
LEAPS options strategies are flexible but extend their expiry dates far into the future. This brings more time for traders to execute their strategies while allowing them to focus on strategic risk management. LEAPS option strategy could be worth exploring if you’re keen to blend the benefits of options with sustainable investment strategies.
In this blog, we’ll discover what LEAPS options trading is, how LEAPS options work, their risks and advantages, and how they’re different from regular temporary options. We’ll also walk through an example of buying a LEAPS call so you can see them in action.
What are Leaps Options?
LEAPS are nothing but option contracts with an expiry date of more than one year, usually LEAPS can last up to 3 years from the date of issuance. The majority of the options expire in weeks or months, butBack in 1990, the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) started offering LEAPS, which gave traders more time to plan out their strategies. Now, you can find them on a wide range of indexes, stocks, and ETFs (Exchange-traded funds).
So, while the LEAPS option strategy may sound complicated, the core idea lies in just long-dated options.
What Does LEAPS Stand For?
LEAPS stands for Long-term Equity Anticipation Securities.
How Do LEAPS Options Work?
Understanding how do LEAPS options work is simple, as they function the same way as any other option, with two major types: call and put.
- LEAPS call option: Gives the holder authority but doesn’t force them to buy the stock at a strike price before the contract expires.
- LEAPS put option: Gives the holder power, but doesn’t pressure them to sell the stock at a set price before expiration.
Time horizon is the only difference between LEAPS and standard options, where LEAPS lasts for one to three years, instead of days or months.
Like other options, the LEAPS contract’s value is based on a range of factors:
- Expiry Date: Longer duration brings more time value, making LEAPS more expensive than temporary options.
- Volatility: Higher volatility amplifies premiums because the likelihood of large price movements increases.
- Strike price related to market price: Determines whether an option is in, out, or at the money.
This longer timeframe makes LEAPS appealing to traders willing to bet on a company’s growth story or use puts as sustainable protection against portfolio declines.
Benefits of Using LEAPS Options
Why would traders buy LEAPS options instead of temporary ones? There are several benefits:
1. More Time for Planning Strategies
With up to three years of expiration date, traders don’t have to worry about temporary market swings derailing their position, giving them time to benefit from gradual stock shifts.
2. Leverage with Less Investment
Purchasing LEAPS calls lets traders regulate the stock’s share for a fraction of the cost of buying the stock outright. If the stock rises significantly, this leverage can maximize returns.
3. Hedging Against Downside Risk
For a portfolio, LEAPS puts can act like sustainable insurance. If a trader owns a large position in stock, purchasing a LEAPS put can protect against a steep decline in value.
4. Flexibility for Sustainable Views
Traders can align their option strategies with sustainable outlooks, such as believing a company would see steady growth over the next two years.
5. Less Pressure of Time Decay
Time decay, which indicates the erosion of an option’s value near expiration, is slower in LEAPS compared to temporary options, particularly in the contract’s initial months.
Risks of LEAPS Options
LEAPS have risks just like any other investment. Some key points to consider are:
1. Higher Costs Beforehand
LEAPS carry higher premiums than temporary options, as they last longer, making them more expensive to buy.
2. Potential for Total Loss
If the stock doesn’t move in the predicted direction by expiration, the LEAPS option can be worthless. Traders risk losing the entire premium paid.
3. Liquidity Concerns
LEAPS may not be as heavily traded as temporary options, resulting in wider bid-ask spreads, which makes it difficult to enter or exit at favourable prices.
4. Intricate Pricing
Many factors, including sustainable volatility expectations, influence LEAPS. This can make pricing harder to comprehend compared to regular options.
5. Opportunity Cost
Investments involved in LEAPS could have been traded somewhere else. If the stock doesn’t move, traders may miss out on better opportunities.
LEAPS Calls vs LEAPS Puts
Both LEAPS calls and puts serve different purposes:
- LEAPS Calls
Best for bullish traders who expect a significant rise in stock prices in the long term.
Brings leveraged exposure to potential returns.
Say, buying a LEAPS call on Tesla stock if you’re certain that it’ll double in three years.
- LEAPS Puts
Best for bearish traders or those seeking insurance on existing holdings.
Protects against downside risk by locking in a minimum selling price.
Say, buying a LEAPS put on an index fund to protect a retirement portfolio from a prolonged market downturn.
To summarise, LEAPS calls involve growth potential while puts involve protection.
LEAPS Options Vs Short-Term Options
| Factors | LEAPS Option | Short-Term Options |
| Expiration | One to three years | Days or months |
| Premiums | Higher because of the time value | Lower |
| Time Decay | Slower in the initial months | Faster |
| Best for | Sustainable strategies, growth bets, hedging | Temporary speculations, quick trades |
| Liquidity | Sometimes lower | Commonly higher |
| Risk of Losses | Entire premium if wrong | Entire premium if wrong |
This table indicates that the biggest differentiator is timeframe, where LEAPS are designed for patient, sustainable strategies, while temporary options cater to active traders.
How to Buy LEAPS Options
Planning to buy LEAPS options is not different from buying the regular ones, but you must keep a few things in mind:
- Selecting the Stock
Decide whether you want to buy LEAPS on an index, ETF, or stock. Choose something you have a strong, sustainable outlook on.
2. Choosing Expiration Date
Look for contracts with one to three years of expiration.
3. Choose a Strike Price
Choose whether you want an at-the-money (expensive but safe) or out-of-the-money (cheaper but riskier) contract.
4. Place the Order Through a Brokerage
Most online brokers let you filter option chains to see available LEAPS contracts.
5. Manage the Position Gradually
Since LEAPS have a longer expiration, traders often hold them for longer periods. But with a changed condition, you can sell the option before expiration.
Example: Buying a LEAPS Call
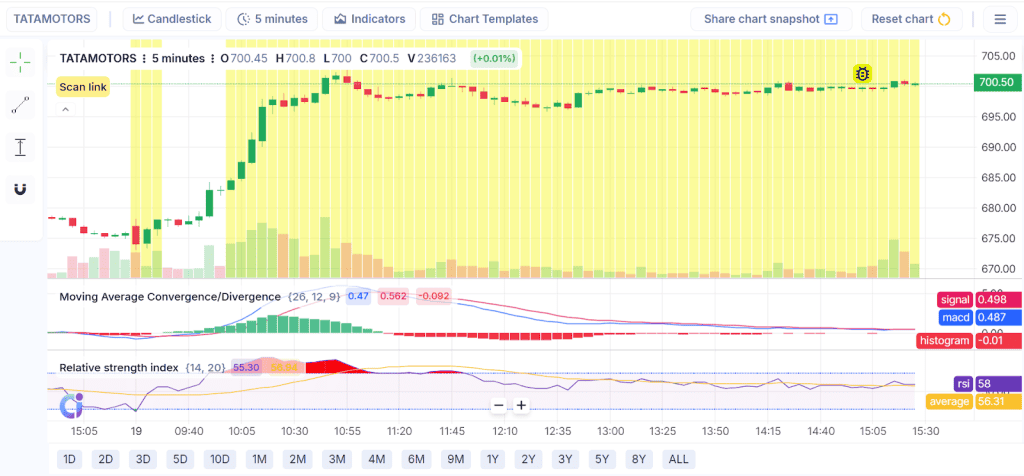
This TATAMOTORS 5-minute chart displays a robust intraday advance accompanied by sideways consolidation. Following a quick rally, the price remains stable near ₹700. Although the MACD indicates that early momentum is fading, the RSI is still over 50, which implies a slight positive bias.
If you think the stock will be trending higher in the next months, this setting could be a good time to buy a LEAP call option, which stands for long-term equity anticipation. Now is an excellent moment to lock in lower premiums before the next leg higher, as the powerful breakout and sustained price levels may imply long-term bullish sentiment.
Conclusion
LEAPS options explained about the unique combination of long-term possibilities and adaptability in options trading, allowing traders to match their option policies with multi-year views. It can be either betting on a company’s growth through calls or safeguarding a portfolio through puts.
While they amplify the costs and risks, their ability to extend the time horizon is what sets them apart. If you’re a patient trader with strong views, LEAPS can be a treasured tool for both hedging and guesswork.
While considering how do LEAPS options work, you must know that, like any other investment plan, you shouldn’t ignore the pros and cons, understand your risk tolerance, and consider LEAPS as part of a diversified strategy. LEAPS options explained make it clear that investors can capture sustainable trends with it while focusing on risk management, if used wisely.
FAQs
LEAPS or Long-Term Equity Anticipation Securities are options contracts that last over a year, sometimes up to three years. They also have calls and puts like regular options. This brings buying or selling options on a stock for traders at a set price. Sustainable traders often use LEAPS to gain exposure to a stock’s probable movement without investing as much capital as owning the shares outright.
Definitely, LEAPS options can be traded before they expire, just like any other options. You don’t have to keep them until maturity. Selling early lets investors grab profits if the option gains value or to minimize losses if the trade moves unfavourably. Since LEAPS last longer, they tend to hold time value better than temporary options, making early exit a practical strategy when market conditions shift.
LEAPS function like traditional options but with longer expirations. With a LEAPS call, traders can control but don’t have to purchase a stock at a set price until expiration. A LEAPS put lets you sell. Since they last up to three years, LEAPS help investors take sustainable positions in a stock’s direction. Premiums are generally higher than short-term options, but they also lose time value more slowly, offering more flexibility.
LEAPS work best with liquid, primarily strong stocks that traders expect to appreciate gradually. Large-cap companies, high-growth technology names, or blue-chip stocks are prevalent choices for their tendency to be more predictable and active options markets. Stocks with solid demand and sustainable growth potential lessen the likelihood of wasted premiums. Highly volatile penny stocks or illiquid names are usually poor candidates since pricing inefficiencies can make LEAPS less effective.
LEAPS can be a good investment for those seeking long-term exposure to a stock with less upfront capital. They offer leveraged returns since a smaller premium controls more shares. But, there’s a catch: if the stock does not move according to your expectations, the option could worthlessly expire. Investors having a strong faith in a stock’s future prospects and wanting to limit capital expense may find LEAPS helpful, provided they understand the risks of time decay and volatility.
The choice depends on the market outlook. If you think the stock will rise significantly over the next one to three years, buy LEAPS calls, but if you anticipate a decline and want downside exposure or portfolio protection, buy LEAPS puts. Many traders use LEAPS calls as a sustainable alternative to stock purchasing, while LEAPS puts can function as hedges against sustainable holdings. The decision should align with your planning, risk tolerance, and financial objectives.
LEAPS options can last as long as three years from the date of issuance. How long you can hold them depends on the contract’s precise expiration date. Traders can hold until maturity or sell earlier with favourable market conditions. Unlike stocks, timing matters in LEAPS, as they have a specific end date. Their prolonged duration makes them appealing for sustainable policies, though traders must consider time decay as expiration approaches.
LEAPS carry several risks despite their long-term nature. The most significant one is the potential loss of the whole premium if the stock moves against your plan. Time decay, though slower compared to temporary options, still wears away value gradually. Volatility modifications can also impact pricing, sometimes undesirably. Unlike temporary options, liquidity may be lower, affecting entry and exit. Lastly, poor stock selection can result in significant downside as leverage amplifies both profits and losses.

