Binary trading sounds tempting, quick bets, fast returns, and that ‘all or nothing’ impulse. But here’s the plot: it doesn’t play by India’s financial rulebook. Behind the sleek apps and flashy promises, most of these platforms operate outside the Indian law.
Therefore, before hitting ‘trade’, it’s worth knowing what the RBI and SEBI actually allow, and why binary trading isn’t a part of that list.
Read further to learn about ‘is binary trading in India’, the legal status of binary trading, and the consequences of trading in binary options.
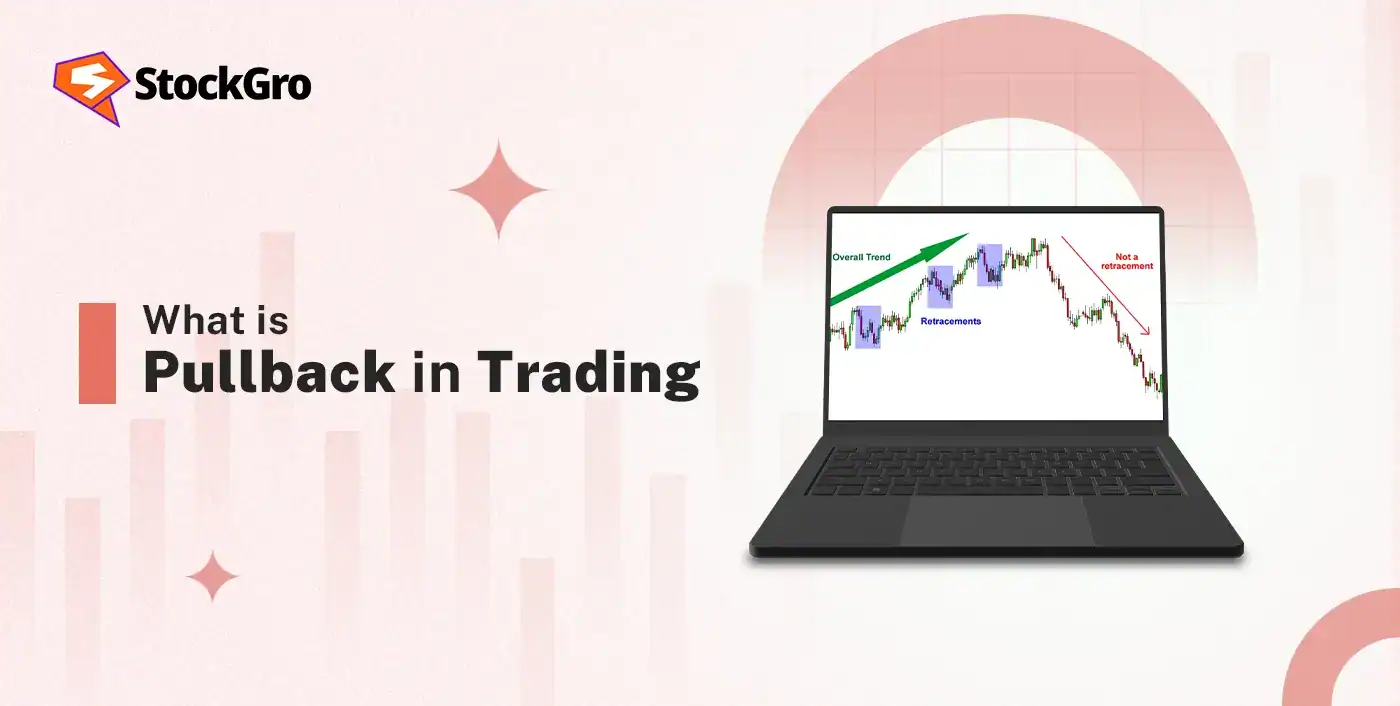
Understanding Binary Trading
Binary trading, involving trading in binary options, represents a form of financial derivative contracts, characterised by high-risk, speculation, and one simple rule: ‘all or nothing’. In binary options trading, options contracts are used to speculate on the underlying price of the assets. It involves speculating on whether the price of an asset will go up or down from the strike price over a given time period.
For example, a trader believes that a company’s stock, currently priced at ₹1,000, will rise above ₹1,010 within the next hour, and invest ₹1,000 in a binary call option offering an 80% return if the prediction is correct.
If the stock closes above ₹1,010, the trader earns ₹800 as profit. However, if the price stays below ₹1,010, the trader loses the entire ₹1,000 investment.
So, as seen in the example, when the prediction is correct, investors receive a fixed-payout, and if it goes wrong, the investor loses the entire investment. These contracts are short-term, ranging from seconds to months, which makes them appealing for short-term gains.
Is binary trading legal in India?
No, binary trading is not legal in India. It is not regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI), or listed on any Indian stock exchanges such as NSE or BSE. And, the RBI has prohibited binary and online trading of foreign exchange through online platforms.
Trading in binary options is considered illegal in India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), which doesn’t allow binary trading through international platforms, and violation may lead to penalties for illegal overseas financial deals.
Legal Status of Binary Option Trading in India
Binary option trading in India is in a grey area, with no regulation, while the RBI restricts trading through online platforms.
- Considered Illegal and unregulated: The binary options are not legal in India and are not available on Indian exchanges like the BSE and NSE. It doesn’t fall under SEBI’s or RBI’s regulatory framework.
- Regulatory prohibition: The RBI has issued guidelines that explicitly prohibit binary options trading and online foreign exchange trading through online platforms.
- Violates FEMA: If any individual engages in binary options trading, especially through online platforms, it is a violation of the FEMA rules.
- High risk and no protection: Binary Trading is done through unregulated international platforms, which involve significant risks for Indian traders, such as withheld payouts and other fraudulent activities, without any regulation or protection from Indian regulators.
Consequences of Illegal Trading
The following consequences apply to anyone dealing through unregulated or unauthorized trading platforms, including binary options and similar online forex schemes.
- Monetary Penalties: If a person is found violating the FEMA guidelines:
- Subject to a penalty up to 3 times of the amount involved, if quantifiable.
- If the amount cannot be determined, the penalty can go up to ₹2 lakh.
- For continuing violations, an additional penalty of ₹5,000 per day applies until the offence continues.
- Criminal Prosecution for Serious Violations: In cases of involvement with foreign assets, securities, or funds held abroad in contravention of FEMA:
- The offenders shall be imprisoned for up to five years, along with a fine.
- This applies when the violation involves significant foreign transactions or assets held outside India without authorisation.
- Civil Imprisonment for Non-Payment: If the imposed penalty is not paid in 90 days:
- The individual can be subjected to civil imprisonment for recovery purposes.
- The duration may extend up to 3 years if the penalty exceeds ₹1 Cr or up to 6 months in other cases.
Legal Alternatives
Investors shall choose these legal financial options for trading, rather than gambling with binary options:
- Standard Options and Futures: These are derivative contracts which provide the investors the right, but not an obligation (call or put options), to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and time.
- Stock Trading: This involves direct buying and selling of shares of companies listed on the NSE and BSE, which is a fully regulated and transparent investment option.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds are for those who want low-risk, investment options for the long-term. These are professionally managed funds spread across various assets, which help to minimise risk and are strictly regulated by SEBI.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): These are funds that track an index and are traded on stock exchanges like regular stocks, offering diversification and regulatory oversight.
Here’s a quick comparison table of what differs binary options trading from other regulated options/derivatives:
| Features | Binary Options | Regulated Options |
| Regulation | Not regulated by any regulatory body | Regulated by SEBI, for fairness and transparency |
| Payout | Offers fixed payout, which involves the all or nothing concept | Here, profit or loss is calculated according to the price movement of the underlying asset |
| Risks | Involves high amount of risk, and is classified as gambling and is prone to fraud acts | These are risky as well, however, managed through regulation such as margin requirement, and position sizing |
| Complications | It involves just hitting the ‘yes/no’ or ‘up/down’ button | It requires in-depth understanding of the market, and strategies |
Bottom line
Binary options trading might look like a shortcut to make profits, but in India, it’s neither legal nor regulated. The RBI and SEBI strictly prohibit such speculative practices under FEMA.
Therefore, traders should avoid these high-risk, unregulated options and rather choose safer, regulated investment options like stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, or standard derivatives for legitimate and transparent returns.
FAQ‘s
No, binary trading is not legal in India. It is not regulated by any regulatory body, such as the RBI or SEBI, and is not listed on any Indian exchanges. Additionally, trading in it through international online platforms violates FEMA, which leads to heavy penalties and legal action.
The penalties for trading in illegal binary options can attract up to three times the amount involved or ₹2 lakh, if unquantifiable, and ₹5,000 per day for continuing offences. In serious cases, offenders will face imprisonment of up to five years and a fine under FEMA provisions.
The SEBI regulates the Indian securities market to ensure transparency, fairness, and investor protection. It oversees stock exchanges, brokers, and mutual funds, implements disclosure rules, prevents fraud, and maintains market integrity through strict compliance measures.
Dabba trading is an unregulated form of trading where transactions are recorded in private ledgers, which bypass official stock exchanges. It is illegal because it evades taxes, lacks regulation from SEBI, offers no investor protection, and facilitates money laundering and fraud.
The legal alternatives to binary trading in India comprise stock trading, futures, and options on NSE or BSE, mutual funds, and ETFs. These are all regulated by SEBI and offer transparency, risk control, and investor protection under Indian financial laws.