Table of contents
Two concepts frequently emerge in the ever-changing world of enterprise financing debt capital and equity capital. These are the bedrock of every company’s financial structure. They provide the power that drives a company’s expansion, growth, and day-to-day operations.
So, what exactly are these terms? In what ways can they affect a company? To top it all off, how are they different from one another? When a business decides between debt and equity financing, it affects its financial stability, ownership control and the ability to bounce back from bad financial circumstances.
This article’s objective is to delve into these two kinds of funding. To help businesses make educated decisions regarding their capital structure and overcome financial challenges, it aims to give a thorough review of debt and equity financing.
Equity financing
A business can acquire funding through equity financing if it sells company shares to investors. Investors can purchase an ownership stake in a company through the sale of shares, which helps the business raise money.
Equity funding can be obtained from a multitude of sources, such as:
- Angel investors
- Venture capitalists
- Crowdfunding platforms
- Initial Public Offerings (IPOs)
Example: Zomato is a prominent Indian meal delivery service company. The equity finance component of the company amounts to ₹8,364 million as of March 31, 2023.
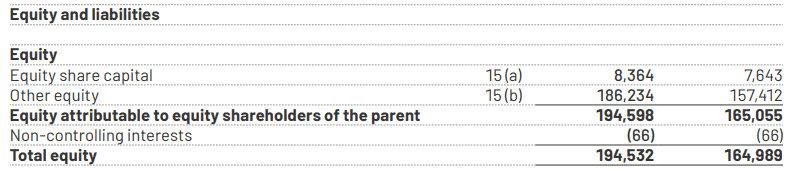
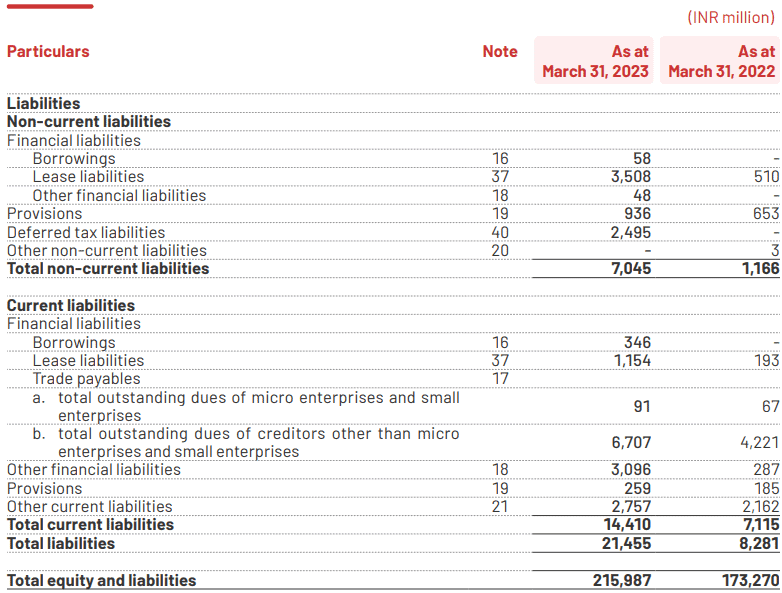
A company can raise capital for operations by issuing shares of common stock, convertible preferred stock, preferred stock, and other equity or quasi-equity instruments. Multiple rounds of equity funding are typical for a startup that manages to mature into a profitable business.
| Pros | Cons |
| Repayment is not obligatory | Ownership in the firm is diluted |
| There will be no additional financial burden on the company. | Control over the company will be lost. |
| Expertise, resources, direction, and connections abound among large investors. | Need to distribute earnings to shareholders |
Debt financing
A business can get the funds it needs through debt financing, which entails either taking out a loan or selling debt instruments. In this loan note, the company guarantees payment of the loan’s principal plus interest.
A variety of sources can provide debt financing.
- Bank loans
- Bonds and debentures
- Factoring
Example:
A well-known Indian automaker is Tata Motors. The debt finance component of the company amounts to ₹ 10,445.70 crores as of March 31, 2023.
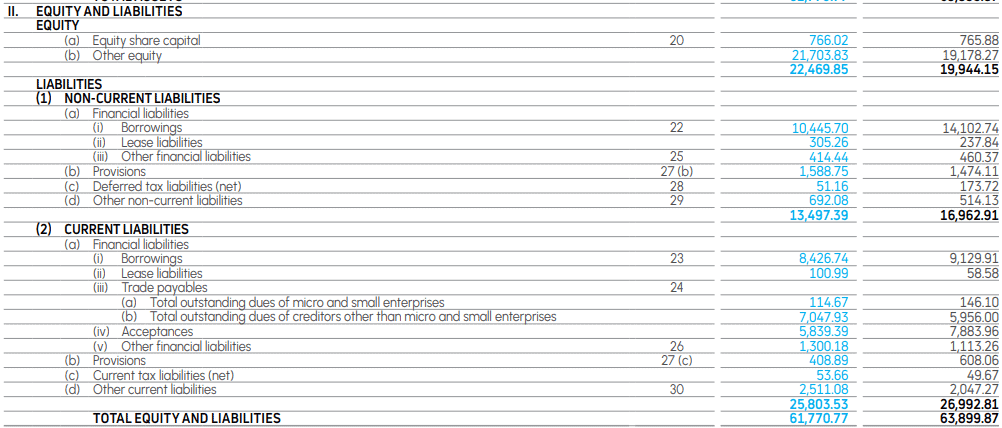
The sale of debt instruments like bonds, bills, or notes is what is known as debt financing. Principal and interest on the loan are due at future dates that the company had specified in the debt contract. Priority is given to paying creditors or holders of instruments in the case of liquidation, rather than shareholders or owners.
| Pros | Cons |
| Maintains ownership of the company | The inability to repay could have a detrimental impact on both personal and business credit. |
| Taxes can be claimed on interest payments. | May end up being expensive for companies with bad credit. |
| Assists in establishing or enhancing a company’s credit | Repay obligations |
| Affordable for those who meet the requirements | Optimal capital structure can be disturbed by increasing debt. |
Difference between equity finance and debt finance: What should you choose?
Speed of accessing funds
While equity financing can take months to finalise owing to valuation and legal considerations, debt financing can get you the money you need in a matter of days or weeks.
Control over business
Lenders do not get ownership stakes when a business uses debt financing, so the owners keep all the control. Raising funds through equity financing often requires giving up some control in return for voting rights and a voice in major decisions.
Qualification criteria
The borrower’s ability to repay a loan is contingent upon a multitude of factors, such as their credit history, cash flow, collateral, and the sustainability of their business. A solid business plan and evidence of past success are more important for equity financing than collateral or cash flow since it is based on the company’s long-term potential.
Repayment structure
Payments are due regularly with debt financing, regardless of how well the company does. Investors in equity financing do not expect immediate repayment; instead, they wait for returns through exit strategies such as acquisitions or initial public offerings (IPOs). However, this type of financing can dilute ownership.
Bottomline
For any company’s financial plan, it is essential to comprehend the difference between debt and equity. A company can raise capital through equity financing by selling a portion of its ownership, as opposed to debt financing, which involves borrowing funds and repaying them with interest.
Cost structure, risk profile, control dynamics, and financial statements are all impacted by each, each with its own set of pros and cons. Businesses must make well-informed financing decisions because the equity and debt fund difference significantly impacts the future of a business.
FAQs
Paying back a loan over time involves accruing interest, which is usually expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. On the other hand, equity interest refers to an investor’s claim on a portion of a company’s profits, often in the form of dividends. While debt interest is a fixed obligation, equity interest is not mandatory and depends on the company’s profitability.
While equity financing does not necessitate repayment, it does dilute ownership through the sale of ownership stakes. It’s often preferred by startups needing substantial capital without increased debt. Debt financing, which involves borrowing money, must be repaid with interest but allows the company to retain full control. It’s typically chosen by established businesses with steady cash flows and the ability to handle additional debt. Therefore, neither is universally better; the choice depends on the company’s needs and situation.
Equity, in the context of finance, is the stake in a company. It is determined by subtracting a company’s total liabilities from its total assets. After a business pays off its debts, the remaining value of its assets is known as equity. It is similar to the net worth of a company’s owners or shareholders. Equity is crucial as it indicates a company’s financial health and is used in key financial ratios.
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is more of a way to invest in mutual funds than a specific kind of fund. It allows an individual to invest regularly in a chosen mutual fund. A debt fund would put most of its money into debt instruments, while an equity fund would put most of its money into stock. Therefore, an SIP can be used for both debt and equity investments, depending on the underlying mutual fund chosen.
