The rise of F&O trading remains strong, with exchanges reporting combined average daily trading volumes hitting an 8-month high of ₹381 trillion in July 2025 despite regulatory curbs. Yet most participants struggle because intraday options move far faster than stocks. Price erosion, timing errors, and leverage amplify small mistakes into large losses. This blog discusses intraday option trading in-detail by outlining working, core strategies, tips and more helping you trade with better preparation.
What Is Intraday Option Trading?
Intraday option trading is a style of trading which focuses on purchasing and exiting option contracts on the same day to capture small intraday price shifts. Traders do not hold positions overnight, which eliminates the risk of gap-up or gap-down openings the next morning. This approach focuses on capturing quick profits from volatility in indices or stock prices before the market session closes.
How Intraday Options Trading Works in India
The intraday option trading method functions through specific operational mechanics and regulatory frameworks found in the Indian market, which include:
- Market hours: Trades are executed between 9:15 AM and 3:30 PM, with all intraday positions requiring square-off before the broker’s cut-off time (typically 3:15 PM or 3:20 PM).
- Indices and stocks: Traders primarily focus on liquid indices like Nifty 50 and Bank Nifty, or highly liquid stocks, to ensure easy entry and exit.
- Settlement: Profits or losses are settled on a “T+1” basis, but the intraday profit/loss is realised immediately in the trading terminal.
- Derivatives contract: You are trading a derivative contract (Call or Put) based on the value being driven by the price of the underlying asset rather than ownership of the asset.
- Price drivers: Option premiums fluctuate rapidly based on the underlying asset’s price, time to expiry (Theta), and market volatility (Implied Volatility).
- Auto square-off: If a trader fails to close a position, the broker’s system automatically closes it at the current market price near the closing bell, often incurring a small penalty charge.
Call & Put Options Basics for Intraday
Understanding the two fundamental types, call and put options is essential for determining market direction and strategy execution, as follows:
- Call option (CE): A Call Option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset; in intraday terms, you buy a CE when you expect the market price to rise (bullish view).
- Put option (PE): A put option grants the buyer permission to sell the underlying asset at the contract’s strike price. For intraday traders, you buy a PE when you expect the market price to fall (bearish view).
- Strike price: This is the fixed price at which the option contract is set; traders must choose between In-the-Money (ITM), At-the-Money (ATM), or Out-of-the-Money (OTM) strikes based on risk appetite.
- Premium: The price you pay to buy the option, which changes constantly during the day based on market movement and time decay.
- Lot size: Options are traded in lots (e.g., Nifty 50 has a specific lot size like 25 or 75 depending on current regulation), meaning you cannot buy a single unit.
Intraday Option Buying vs Option Selling
The main differences between the intraday option buying and option selling strategy have been outlined below:
| Feature | Intraday option buying | Intraday option selling |
| Capital requirement | Low (Premium value only) | High (Full SPAN + Exposure Margin) |
| Risk profile | Limited to premium paid | Theoretically unlimited |
| Profit potential | Unlimited (if trend is strong) | Limited to premium received |
| Key profit driver | Momentum and high volatility (Delta) | Time decay (Theta) and low volatility |
| Success probability | Lower (requires sharp moves) | Higher (profits in sideways markets) |
| Market condition | Ideal for trending/breakout markets | Ideal for range-bound/consolidating markets |
Margin & Leverage Rules in Intraday Options
Margin requirements are strictly regulated to manage the high risk associated with derivatives trading, and current rules as of 2025 operate such as:
- No additional leverage: Brokers are no longer permitted to offer extra leverage beyond what is specified by SEBI and exchanges. Intraday option traders must adhere to the full margin requirement prescribed for their positions.
- Market-wide position limits (MWPL): New rules effective October 2025 calculate MWPL based on free float or cash delivery volume, with stricter monitoring to prevent concentration risk.
- Position limits: Individual investors must stay under specific caps (e.g., 10% of MWPL) for single stocks to avoid regulatory violations.
- Ban periods: Stocks exceeding 95% of MWPL enter a ban period where no new positions can be taken, only existing ones can be squared off.
- Premium-only margin for buyers: Option buyers are required to pay 100% of the premium amount upfront. This is the maximum loss for a buyer; hence, no additional margin or leverage is allowed.
- Leverage cap: As of 2025, maximum permissible intraday leverage is effectively 1x for options trading, meaning traders must maintain the full required margin; speculative or high-leverage intraday products are prohibited.
Most Profitable Intraday Option Trading Strategies
Success in the intraday option trading often depends on deploying specific strategies that align with the existing market conditions, include the following:
- Momentum trading: This consists of identifying stocks or indices moving strongly in one direction and entering a trade to ride the wave, exiting as soon as signs of reversal appear.
- Breakout strategy: A trade is triggered when the price cuts through a crucial support area with high volume, signalling a potential sharp move in that direction.
- Reversal strategy: This targets profits by identifying overbought or oversold conditions (often near support/resistance zones) and betting against the current trend, though it carries higher risk.
- Gap and go: Traders look for stocks that open with a significant price gap (up or down) from the previous day’s close and trade in the direction of the gap if momentum sustains.
- Moving average crossover: A simple trend-following method where buy or sell signals are generated. This occurs when a faster-moving average intersects with a slower one.
- Bear put/pull call spreads: These are hedging intraday trading strategies involving buying and selling options simultaneously to limit risk, often recommended for volatile indices like Nifty.
Scalping Strategy for Options (Fast Entry/Exit)
This high-speed technique uses specific indicators to capture small price changes, such as:
- VWAP support: Traders use the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) as a dynamic support or resistance line to time entries when the price bounces off it.
- EMA crossovers: A common setup involves the 9-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) crossing the 20-period EMA to signal short-term momentum shifts.
- Timeframe selection: Scalpers typically use 1-minute or 5-minute charts to spot immediate price action opportunities.
- Quick profit booking: The goal is to capture small moves (e.g., 5-10 points in premium) rather than waiting for large trends.
- Volume confirmation: Trades are only taken when there is a spike in volume, ensuring there is enough liquidity for a fast exit.
- Strict stop-loss: Stop-losses are placed very tight, often just below a recent swing low or support level, to minimise damage from false signals.
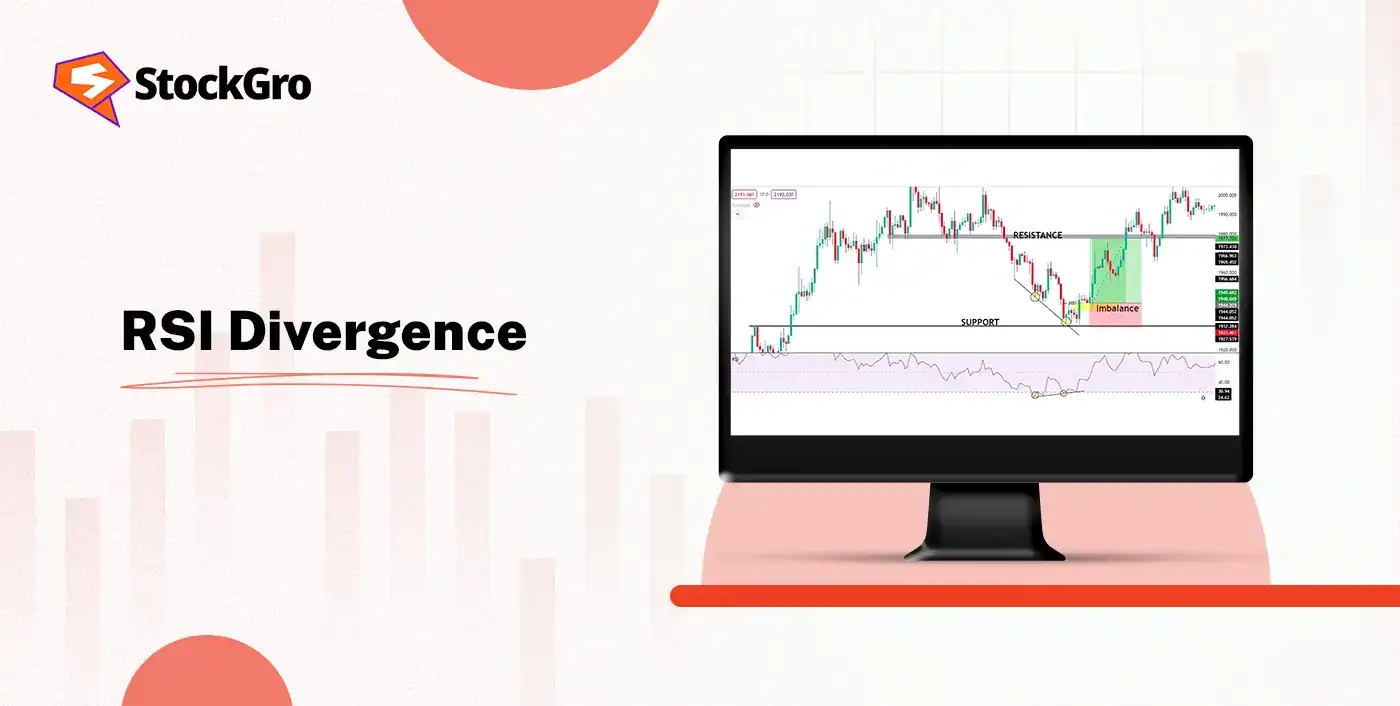
5‑Minute Setup: RSI + MACD for Weekly Options
This specific setup utilises a 5-minute chart timeframe to identify high-probability trend reversals or continuations for weekly expiry options. The trader combines the Relative Strength Index (RSI) with the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator. First, check the RSI; an RSI above 70 indicates overbought conditions (potential sell/put buy), while below 30 indicates oversold (potential buy/call buy). However, RSI alone is not enough.
The signal is confirmed only when the MACD line crosses the signal line in the corresponding direction (e.g., MACD crosses below the signal line for a sell). This two-step confirmation method helps screen out frequent false alerts seen in intraday option trading. Entries should be timed when volume supports the move, and exits should be taken when the indicators show signs of cooling off or reversing.
Bank Nifty & Nifty Option Intraday Strategy
Index-specific approaches focus on key derivative data and levels such as:
- PCR analysis: Traders monitor the Put-Call Ratio (PCR); a ratio above 1.3 often indicates bullish sentiment, while below 0.7 suggests bearish sentiment.
- Option chain data: Analysing Open Interest (OI) buildup at specific strikes helps identify strong support (high Put OI) and resistance (high Call OI) levels.
- Premiums & theta: Traders often prefer “At-The-Money” (ATM) strikes for Nifty options to balance liquidity and premium sensitivity (Delta).
- Checking variability: Avoiding trades during low volatility periods (low VIX) prevents premiums from eroding due to time decay.
- Level breakouts: Entries are often timed around the breakout of the previous day’s high or low, which act as critical psychological barriers.
Intraday Premium Decay Strategy for Sellers
Implementing this strategy requires following a structured workflow to maximise time value benefits as follows:
- Identify market condition: Traders analyse technical charts to confirm the market is in a sideways or range-bound phase, avoiding this strategy during high-momentum trends.
- Select strike prices: Participants choose deep Out-Of-The-Money (OTM) strikes for both Call and Put options, ensuring they are far enough from the current price to remain safe.
- Initiate short strangle: The trader sells (writes) both the selected Call and Put options simultaneously to collect premiums from both sides.
- Set stop-loss: A strict stop-loss is placed for each leg, typically at 25% to 30% of the premium value, to protect against sudden market moves.
- Monitor decay: As the day progresses, the time value (Theta) erodes the premium of both options, generating profit even if the market price barely moves.
- Square off: The positions are closed manually before the market ends to lock in the intraday option trading gains derived from the decayed premiums.
Trade Planning Rules
A disciplined trading plan requires defining clear parameters before execution such as:
- Pre-defined entry/exit: Traders must determine the exact price levels for entering and exiting a trade before placing the order.
- Capital allocation: A rule of thumb is to never deploy more than 50% of total trading capital in a single day to preserve liquidity.
- Risk per trade: An effective intraday option trading relies on risking only 1-2% of total capital on any single trade.
- Trading journal: Maintaining a record of all trades helps in analysing mistakes and refining strategies over time.
- Avoid overtrading: Limiting the number of trades per day (e.g., maximum 3) prevents emotional decision-making and excessive brokerage costs.
- Emotional control: Traders should step away after a series of losses rather than attempting “revenge trading” to recover funds immediately.
Strike Price Selection Rules
Choosing the correct strike price is important because it dictates the option’s delta and liquidity, as follows:
- At-the-money (ATM): Often the best balance of premium cost and sensitivity to price movement, making it popular for intraday option trading.
- In-the-money (ITM): These contracts cost more but have a stronger delta, making their movement closely mirror the underlying asset.
- Out-of-the-money (OTM): Cheaper premiums but lower probability of profit; usually avoided for intraday buying unless a massive momentum shift is expected.
- Delta values: A Delta of 0 to 0.5 is ideal for option buyers to ensure the premium moves sufficiently with the underlying asset.
- Expiry distance: Avoiding deep OTM strikes on expiry days is crucial as they are likely to expire worthless.
- Liquidity check: Always select strike prices with high open interest and volume to ensure you can enter and exit trades instantly without slippage.
Stop‑Loss & Target Setting for Intraday Options
Risk management in intraday option trading relies on precise order placement such as:
- Technical stop-loss: Placing stops based on chart levels, such as below the recent swing low or a key support level, rather than a random number.
- Percentage rule: Setting a maximum loss limit per trade, commonly between 5% to 10% of the premium paid.
- Risk-reward ratio: Aiming for a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2 or 1:3 ensures that one profitable trade can cover multiple small losses.
- Trailing stop-loss: As the position moves into profit, the stop-loss is moved higher to lock in gains and protect against reversals.
- System stops: Using system-based stop-loss orders (SL-M) ensures the exit is triggered automatically even during sudden volatility spikes.
- Target levels: Profit targets are identified using resistance levels, pivot points, or Fibonacci extensions before entering the trade.
Position Sizing & Risk‑Reward Model
A structured risk management in trading approach protects capital by defining loss limits and profit potential before execution such as:
- Risk per trade: To stay consistent, traders restrict individual trade losses to about 1–2% of overall capital to maintain trading discipline.
- Risk-reward ratio: The usual benchmark is a 1:2–1:3 ratio, ensuring the reward outweighs the risk by two or three times.
- Lot size formula: The number of lots is calculated by dividing the maximum risk amount by the stop-loss points per lot.
- Capital segmentation: Allocating only a portion of funds to a single trade prevents a total wipeout from one bad decision.
- Drawdown cap: Setting a daily loss limit acts as a circuit breaker to stop trading during poor market conditions.
Best Time To Trade Options — Avoid First 20 Min & Last 30 Min
Timing the entry and exit is critical to avoid unpredictable volatility and technical glitches as follows:
- Initial variations (9:15–9:35 AM): The first 20 minutes often see erratic price swings due to overnight news and pre-open order settlements, leading to false signals.
- Price discovery: Indicators like RSI and MACD are unreliable early on as the market attempts to establish the day’s trend and equilibrium price.
- Ideal window: The period from 10:00 AM to 2:30 PM is typically the best time for trading as it offers stable trends and consistent option premiums suitable for intraday option trading.
- Square-off spikes (3:00–3:30 PM): Broker auto-square-off systems trigger mass exits in the last 30 minutes, causing sudden and irrational price movements.
- Exit liquidity: Attempting to trade near the close increases the risk of getting stuck or receiving poor fill prices due to high volatility.
Real‑Life Intraday Option Trading Case Study
In July 2025, Jane Street demonstrated a high-frequency scalping approach on Indian indices like Nifty and Bank Nifty to exploit short-term volatility. The strategy involved executing thousands of rapid trades on near-ATM options, focusing on capturing small price differences rather than long-term direction. In line with 2025 regulations, the firm paid full upfront premiums for purchases and maintained strict SPAN plus exposure margins for selling, ensuring operations remained fully compliant while engaging in high-volume intraday option trading.
The core of this strategy rested on exploiting market microstructure, such as bid-ask spreads and minor index fluctuations of 0.5% to 1%. Trades were typically held for just 5 to 30 minutes to reduce exposure to adverse price shifts. By leveraging automated systems that triggered exits at pre-set profit or loss levels, the firm managed risk in real-time without holding positions overnight. This approach highlighted how institutional players prioritise speed and execution efficiency over leverage to generate consistent returns in the regulated derivatives market.
Conclusion
This trading style focuses on quick price movements within market hours. Intraday option trading ensures all positions are closed before the day ends. It avoids the uncertainty of overnight market gaps. The process demands steady attention and a clear plan to navigate daily fluctuations effectively.
FAQs
Intraday option trading involves buying/selling options contracts within the same day, squaring off before close to capture short-term volatility without overnight risk. Focuses on indices like Nifty/Bank Nifty using momentum strategies.
Beginners face high risks from premium decay, leverage, and fast moves. Requires chart reading, Greeks knowledge, and discipline. 93% F&O traders lose money; start with paper trading, master the cash market first before options.
Option buying suits trending markets (unlimited profit, capped risk to premium). Selling profitable in range-bound markets (higher win rate via theta decay) but needs high capital/margins and unlimited risk. Buying is safer for beginners.
RSI+MACD on 5-min charts: Buy calls when RSI >30 + MACD bullish crossover; puts when RSI <70 + bearish crossover. Use PCR, option chain OI for strikes. VWAP support + volume confirmation. 1:2 risk-reward.
ATM strikes (Delta 0.5-0.7) balance premium/liquidity. ITM for higher delta/safety, OTM for cheap leverage. Check high OI/volume strikes. Avoid deep OTM near expiry. Match direction: CE bullish, PE bearish views.
5-minute charts ideal for RSI/MACD setups. 1-minute for scalping VWAP/EMA crossovers. 15-minute filters noise for trend trades. Avoid the first 20 min (9:15-9:35) and the last 30 min (3:00-3:30) due to volatility.
One to two lakh minimum for 1-2 lots (Nifty/Bank Nifty). Covers premiums/margins. Risk 1-2% per trade (₹2,000 max loss). Never exceed 50% capital daily. Full upfront premiums required per 2025 SEBI rules.