
The asset prices can get chaotic, but the option premiums usually reveal the real mood of the market. When things look mildly bullish, not moon-shot bullish, just steady, this strategy becomes a clean way to earn while keeping the risk defined.
A bull put spread strategy is built by selling a put with the higher strike and pairing it with a put bought at a lower strike to limit potential losses. Both legs move together to build a position that benefits when the price stays firm or edges upward. It’s a smarter way to trade a gentle bullish view without overexposing the account or waiting for huge rallies that may never show up.
Once the bull put strategy is understood, how two put options balance each other out, spotting good setups, choosing the right expiry, and managing risk becomes way easier, even in fast-moving markets.
This blog breaks down what the bull put spread strategy is, how it works, when to use it, its advantages and drawbacks, and how adding simple stop-loss protection keeps things even tighter.
What is a Bull Put Spread Strategy?
The bull put spread strategy is an options trading strategy that fits a steady to mildly bullish market. It works by selling a put at a higher strike and, at the same time, buying a put at a lower strike, both expiring on the same date.
This setup brings in an upfront credit, giving a limited profit equal to that credit. The loss is also limited, at the gap between the two strike prices after subtracting the credit earned.
Let’s assume a stock is trading at ₹1,000. A trader sells a ₹980 put (higher strike price) and collects a credit of ₹20 and buys another ₹960 put (lower strike price) for a ₹10 credit. Here, the trader collects a net credit of ₹10. If the stock stays above ₹980 at expiry, he gets to keep the entire ₹10, and his maximum loss is held at ₹20, the strike difference of ₹20 minus the ₹10 credit, if the stock falls below ₹960. This setup works well when it is expected that the price will hold above support.
How Does the Bull Put Spread Work?
- Selling a put option: The trader writes a put with a higher strike price to earn a premium. This becomes the at-the-money or in-the-money part of the spread.
- Buying a put option: Simultaneously, they buy a put option with a lower strike price to act as a hedge and limit risk, while paying a premium for it. This is the out-of-the-money leg.
- Net credit: The premium earned from the higher strike put outweighs the premium spent on the lower strike put, creating a net credit when the position is opened.
- Expiration and underlying: In this setup, the two options must be tied to the same underlying asset and share the same expiration date for the strategy to work properly.
Example of a Bull Put Spread Strategy
Here’s how a bull put spread actually looks when plotted on a payoff chart. In this example, a trader builds a spread with the following strikes, at one expiry date:
- Sell the 6,970 Put for 117
- Buy the 6,850 Put for 39.5
This creates a net credit of 77.5 (117 – 39.5), which is the maximum profit the trader can earn from this trade.
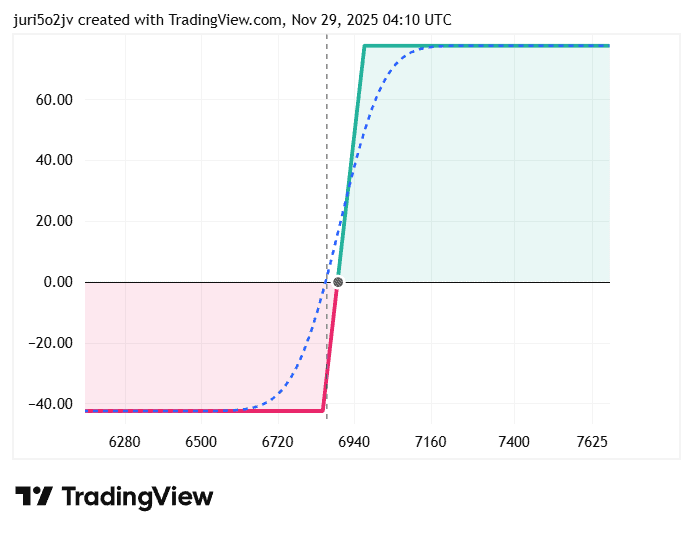
The chart below visualises the spread:
- The flat green zone shows the area where the trade makes money. If the put option stays above 6,970 at expiry, both the puts expire out of the money, and the full credit will be kept by the trader.
- The red zone below 6,850 reflects the maximum loss. If the price drops under the long put, the spread widens fully, and the loss is 42.5 points, the strike difference minus the credit received.
- The transition slope between 6,970 and 6,850 is where profit slowly fades as price moves lower.
- The break-even price is at 6,892.5, which is simply the short strike minus the credit (6,970 – 77.5).
When to Use a Bull Put Spread
- Slightly bullish market: When the trader expects the price to rise slightly or stay steady, but not fall sharply.
- High implied volatility: The trader can collect a larger premium by selling puts when the implied volatility is high.
- Sideways or consolidation phase: If the market is moving in a range, the strategy allows for earning income.
- Strong support zone: If the trader believes the price will not fall below a specific support level.
- Accumulate stock at a lower cost: The premium collected reduces the effective cost of buying shares if the put is exercised.
Advantages of a Bull Put Spread
- Defined and Limited Risk: The maximum possible loss is limited and known at the outset of the trade, making it a safer strategy than selling a naked or uncovered put.
- Upfront Income Generation: The trader receives a net premium or credit while initiating the position, since the sold put pays more than the bought one.
- Benefits from Time Decay: This time decay benefits the trader because if the stock stays above the higher strike and both options expire worthless, the entire credit remains in the trader’s pocket.
- Profitability in Various Scenarios: The strategy works as long as the price stays above the break-even level at expiration, even if it rises, stays flat, or dips slightly. That’s why it fits a neutral-to-moderately bullish market view.
Drawbacks of a Bull Put Spread
- Limited profit potential: The profit potential is limited to the net credit received when opening the trade, meaning the trade cannot fully benefit from a large upward move in the underlying asset.
- Risk of loss: If the underlying falls below the lower strike by expiry, the trader takes a loss equal to the gap between the two strikes after subtracting the net credit earned.
- Inability to capture large gains: Since the profit is limited and the trader will miss out on any gains above the short put’s strike price, even if the stock price moves higher.
- Complex execution: The strategy requires a good understanding of options trading and financial markets in order to be executed correctly.
Adding a Layer of Protection with Stop-Loss Orders
Adding a stop-loss order to a bull put spread provides a safety net by automatically closing the position if the underlying asset’s price falls to a predetermined level, limiting losses. Since a bull put spread is a defined-risk strategy, the long put already acts as a hedge, but a stop-loss can exit the trade early if the price moves against expectations, even before the long put’s maximum potential is reached.
The traders might set a stop-loss based on the underlying asset’s price or the spread’s premium value to manage risk and remove emotion from the decision to close the position.
How to add a stop-loss to a bull put spread?
- Understanding the strategy: The setup works as long as the underlying trades above the higher strike, and the long put acts as a safety net to cap the downside.
- Setting a trigger price: The stop-loss trigger is the price for the underlying asset at which a trader might want to exit the trade if the price falls below it.
- Placing the order: The stop-loss order is placed to sell the entire spread when the underlying asset’s price reaches the predetermined trigger price.
Summary
A bull put spread is a defined-risk options strategy, which is built for neutral to slightly bullish markets. It’s built by selling a put at a higher strike and buying another at a lower strike, both expiring together, resulting in a net credit. The maximum profit is the credit received, while the loss is held in check by the long put.
The spread benefits from time decay and works well when prices hold above support. The traders use it to earn steady income with controlled downside, especially in stable or mildly rising markets.
FAQ‘s
The bull put spread is an options strategy where a trader sells a higher-strike put and buys a lower-strike put of the same expiry, with a goal to earn a net credit while keeping the risk defined and limited.
In the bull put spread strategy, the sold put brings in premium, and the bought put limits the losses. The trade makes money if the price stays above the short strike by the expiry.
The bull put spread strategy works best in neutral to mildly bullish markets, during consolidation phases, or when it is expected that the price will hold above a strong support level.
The maximum profit that can be earned in a bull put spread is the net credit received, and the maximum loss is the strike difference minus that credit.
In order to calculate the breakeven point in a bull put spread, subtract the net credit from the short put’s strike price. The resultant value is the breakeven at expiry.
Yes, in a bull put spread, the long put holds the downside risks, so the loss is known in advance, and it cannot exceed the defined spread width, minus the credit.
In a bull put spread, if the price stays above the short strike, the spread expires worthless, and the full credit is kept, but if it drops below the long strike, the spread hits its maximum loss.
Yes, any trader, be it a beginner or an experienced trader, can utilise a bull put spread as long as they understand strike selection, expiry, and risk. It is considered a beginner-friendly credit setup because both the profit and loss are predefined.

